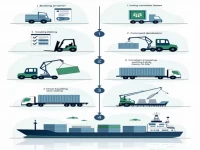
Tianjin Sea Freight Full Container Export Process Analysis
This article outlines the basic procedures for full container ocean export at Tianjin Port, including booking, container pickup, loading, customs declaration, consolidation, and shipping. Each step is interconnected to ensure the safety and compliance of the transportation process. The importance of customs supervision is particularly emphasized, aiming to reduce smuggling risks in cargo management and ensure the smooth progress of all formalities.